Microservices are a way to break down a monolithic application into small, simple and independent services that work together, where each is responsible fro a specific function. This brings scalability
The basic concept of microservices also talks about the
Features of MicroServices:
- Service Oriented Approach
- Componentization via Services
- Organized around business capabilities
- Products not projects
- Smart end point dump pipes
- Decentralized governance
- Decentralized data management
- Infrastructure automation
- Design for failure
- Evolutionary design
Tools for building Micro Services
- Scriptable cloud infrastructire to automate continuos delivery release pipelines
- Reliable Messaging Infrastructire to allow service chirography
- Highly productive development framework
- Containerless runtime to allow deployment of one executable per service
Spring Boot
- It makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications.
- Embed Tomcat or Jetty Directly (no need to deploy WAR files)
- Automatically configure Spring whenever possible
- Provide production ready features such as metrics, health checks and externalized configuration.
Create a Spring Boot Application :
The basic concept of microservices also talks about the
Features of MicroServices:
- Service Oriented Approach
- Componentization via Services
- Organized around business capabilities
- Products not projects
- Smart end point dump pipes
- Decentralized governance
- Decentralized data management
- Infrastructure automation
- Design for failure
- Evolutionary design
Tools for building Micro Services
- Scriptable cloud infrastructire to automate continuos delivery release pipelines
- Reliable Messaging Infrastructire to allow service chirography
- Highly productive development framework
- Containerless runtime to allow deployment of one executable per service
Spring Boot
- It makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications.
- Embed Tomcat or Jetty Directly (no need to deploy WAR files)
- Automatically configure Spring whenever possible
- Provide production ready features such as metrics, health checks and externalized configuration.
Create a Spring Boot Application :
References :
This is an example to package and run a spring boot application as a microservice. It will bring up the spring application with an embedded web server. The executable jar includes all the required libraries to run this as an independent service. Following are the details :
- The code can be downloaded from github:
https://github.com/SanjayIngole/demo-microservice-springboot/archive/master.zip
- There is runnable microservice jar as well that can be downloaded from following location:
https://github.com/SanjayIngole/demo-microservice-springboot/blob/master/DemoMicroServices/target/demo-0.0.1.jar
- To run this microservic. It will bring up the spring application with an embedded web server.
java -jar demo.jar
- A test page can be used to upload the sample xml and obtain JSON response.
https://github.com/SanjayIngole/demo-microservice-springboot/blob/master/DemoMicroServices/src/main/resources/testpage.html
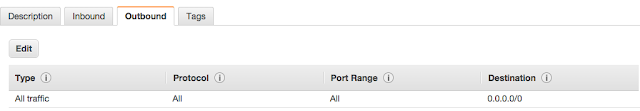
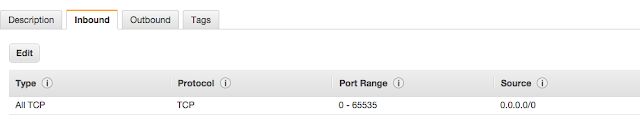
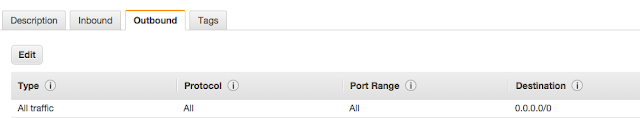
- You can use a docker or boxfuse to deploy this on cloud. I use boxfuse to deploy my microservices to aws. You can setup a boxfuse account (https://console.boxfuse.com/) and configure your aws instance, and then download boxfuse command line client.
- Package your project using maven, which will package all dependent jars in one file.
- mvn package
- And then deploy it using boxfuse command, this deploy this application on configured aws instance.
- boxfuse run demo:0.0.1